Product Display
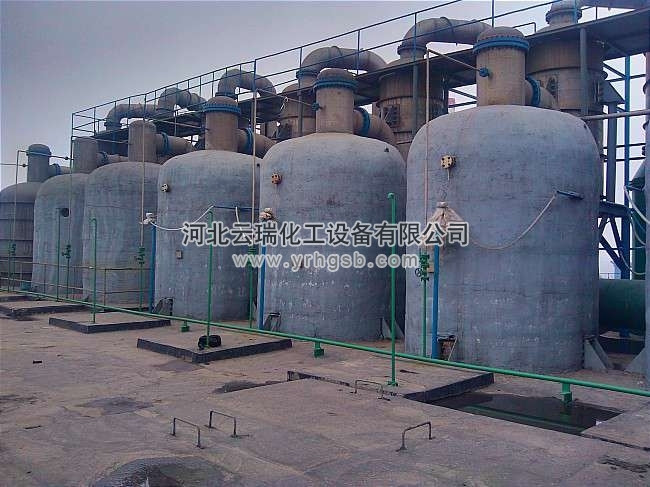
The evaporation of alkali sulfide has evolved from the initial large pot open flame evaporation to the rotary film evaporator evaporation, and further developed into vacuum continuous evaporation. It not only overcomes the disadvantages of low thermal efficiency, high energy consumption, high labor intensity, serious pollution, poor operating conditions, large fluctuations in product quality, and poor product stability of large pot open flame evaporation, but also overcomes the difficulties in material selection, installation, and maintenance of rotary film evaporators.
The vacuum continuous evaporator uses low-pressure steam as the heat source (0.65MPa), which can achieve the concentration and evaporation process of sodium sulfide in a vacuum state. The sodium sulfide evaporation and concentration process has a closed system, can operate continuously, improved operating conditions, high degree of automation, and does not cause any pollution to the environment. The evaporation system adopts forced circulation, and the liquid flow rate inside the tube is high, thereby ensuring that the heat exchanger does not crystallize or scale, which is very effective in improving the heat transfer coefficient. In addition, the heating tube is located in the circulation pipeline, which is easy to clean.
drying and tower.

 中文(簡體)
中文(簡體)